Turning Data into Information Using ArcGIS 10.0 module 4: Generating and comparing IDW and Kriging surfaces
Problem: Generating surfaces from samples with an elevation attribute is an important operation in GIS. There are multiple statistical methods and each may have advantages and disadvantages in a particular scenario. IDW is computational less intense, but also may be less accurate depending on the physical region and samples taken. The Kriging method may give a more accurate result but it may take much longer to compute. Any statistical method to interpolate a surface based on samples will do a poor job if the sampling technique was poor.
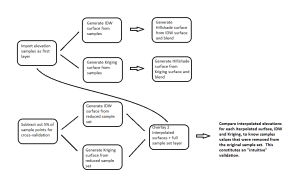
Analysis Procedures: A sample set map file is opened in ArcMap. This sample set is used to independently generate an IDW surface and Kriging surface with the respective Spatial Analyst tools. Each surface is then separately used to create a Hillshade layer with and the interpolated layer in each case is set to a 45% transparency and set over the hillshade layer to create an elevation map with relief. As a cross-validation, the 5% of the sample points are removed from the original sample set and this set is used to again interpolate surfaces using the IDW and Kriging tools. Each of these surfaces is now compared against the known height values associated with the points that were removed from the original sample set.
Results: The sample set represents a set of coordinates across a given physical space with actual measurements associated with them. In this case elevation, in meters, is known for each sample:

The IDW Spatial Analyst tool interpolates the sample set using IDW interpolation (left). Colors shown represent low lying regions (green) to high elevations (white). The Hillshade tool is used to create a hillshade from the IDW surface. The IDW surface is then set at 45% transparency and laid over the hillshade layer to create an elevation map with relief (right):
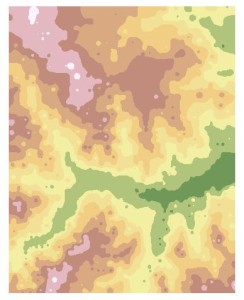
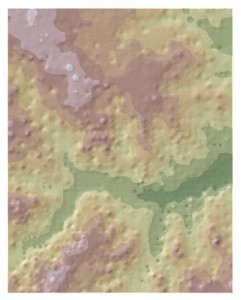
The Kriging Spatial Analyst tool interpolates the sample set using Kriging interpolation (left). The Hillshade tool is used to create a hillshade from the Kriging surface. The IDW surface is then set at 45% transparency and laid over the hillshade layer to create an elevation map with relief (right). The two surfaces over hillshade show significant difference, with the Kriging based map presenting a smoother landscape. Which is more accurate though?
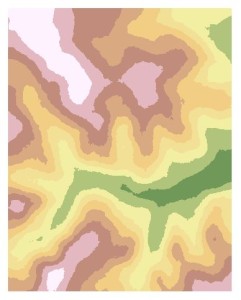

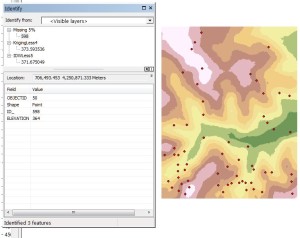
As a simple validation and comparison of the interpolation methods, 5% of the sample points are randomly removed from the original sample set. IDW and Kriging surfaces are generated from this reduced sample set and can be used to validate the predicted elevations, by each method, against the known measured values for those missing sample points. Here is shown a typical difference, where the measured value was 364 meters and Kriging predicted 373.6 meters and IDW 371.7 meters. Neither technique was clearly superior over the other in this small test.
Application & Reflection
Problem description: Map the floor of Lake Jordan.
Data needed: Sonar depth samples taken at regular intervals in a grid like pattern across the entire surface of the lake.
Analysis procedures: Use IDW and Kriging techniques to generate a surface of the lake floor from the sample data points.