Turning Data into Information Using ArcGIS 10.0 Module 2: Interacting with a GIS display using feature selections
Problem: GIS digital maps are typically comprised of many layers of data each one of which can contain significant information. The maps are not limited by a fixed boundary, as is a paper map, and areas can be zoomed in or out to reveal more or less detail as appropriate. A typical problem when creating purposeful static map is what information to include. Understanding how to find, add and remove features is critical to achieving this goal.
Analysis Procedures: A map file is opened in ArcMap which contains multiple layers of features typically associated with a metro area. A specific college is identified from a colleges layer and then a buffer zone of 1 mile is created around that college to look at nearby Hospitals, City Attractions ad RR Stops. Different techniques are reviewed to identify a specific attraction and which hospitals are nearby.
Results: This module reviews some fundamental ways to harvest information from maps. It touches on some tools that can be used to identify relationships between objects and also demonstrates that there is often more than one approach when trying to achieve some outcome.
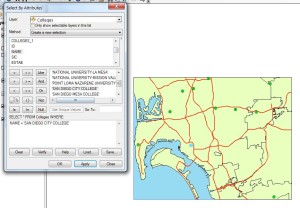
After loading the .mxd file a single college is identified from the colleges layer. This is done via the Select By Attributes selection window which queries the related Colleges table which a logical operation that tests the NAME field for equivalence to desired name- “SAN DIEGO CITY COLLEGE”. The query is shown in the window as a SELECT statement and the map shows all of the visible colleges in green and the selected one in blue:
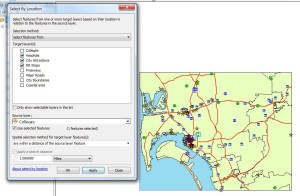
A buffer is created 1 mile in radius around the selected college with a Select By Location query. 3 layers are targeted for this location selection and these can be seen in the Select window (left). The image on the right shows City Attractions (purple) that are within the one mile buffer of the selected college:
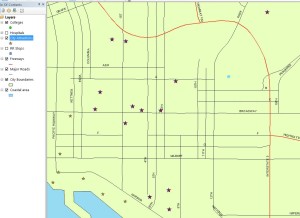
Application & Reflection
Problem Description: Identify small lots in a subdivision adjacent to creeks.
Data needed: A parcel layer that represents lots that also shows lot sizes. A water layer that shows creeks and streams.
Analysis procedures: Buffer the streams and select all lots that overlay the stream buffer. From this selection select lots that a smaller than a specified threshold.